Frequently Asked Questions
Please find here the frequently asked questions (FAQ) in electronics production... The questions are categorized into topics below.
Wave Soldering
Please see below to find out more about Wave Soldering.
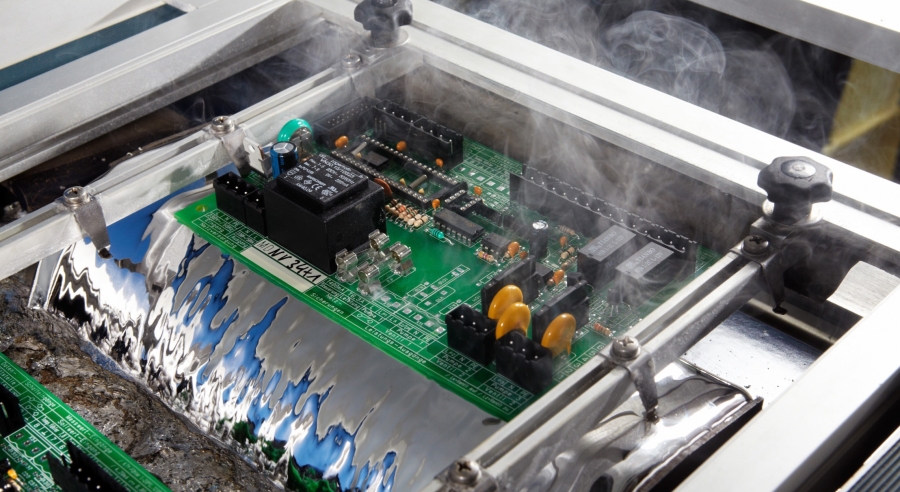

Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are often wave-soldered. However, some conditions make wave soldering difficult or expensive. Let’s take a look at the difference between wave and selective soldering.
Wave Soldering
Wave soldering is a bulk process where PCBs are passed over a wave of molten solder to attach through-hole (THT), surface mount technology (SMT), and mixed assemblies to circuit boards.
The major downside of wave soldering is the limited ability to define process parameters, which leads to poor solder joint quality and diminished product reliability. This limitation forces a one-size-fits-all approach to application and makes selectivity impossible. Solder washes over the board, applied universally, even where it is not required.
Additional, wave soldering disadvantages include:
High solder consumption
High flux consumption
High power consumption
High nitrogen consumption
An increase in post-wave solder rework
Masking of sensitive areas on PCB assemblies
Cleaning of wave solder aperture pallets or masks
Cleaning of soldered assemblies
With these significant disadvantages, wave soldering operating costs can be significantly higher when compared to selective soldering.
Selective Soldering
Selective soldering, also known as mini-wave soldering, offers cost-effective, repeatable results for THT and mixed technology soldering applications. Soldering points are individually programmed and monitored to control flux volumes and soldering time. And it is the only reproducible method for soldering THT components on a two-sided PCB assembly.
Selective soldering typically consists of three stages:
Fluxing or the application of liquid flux.
Preheating of the PCB assembly.
Soldering with a site-specific solder nozzle.
Selective soldering makes it possible to solder a wide range of PCB assemblies with advantages, including:
Secure and fast process optimization
Reliable solder joint creation without overheating components
Guaranteed process repeatability
The elimination of expensive wave solder pallets
The ability to solder around tall parts with tight spacing
The ability to solder dense concentrations of THT pins
All Nordson SELECT solutions come standard with nitrogen inerting, a titanium solder pot to resist the corrosive effects of aggressive lead-free solder alloys, and intuitive system software you can set up in minutes without prior experience.
Why Nordson?
You can be confident when choosing Nordson as your selective soldering partner. Our commitment to innovation, investment in R&D, and customer service excellence allow us to deliver consistent performance and reliability.
Download the Wave vs Selective Soldering Process Comparison Guide for additional process and cost information.
Have Another Question?
Please share your contact information with us. Our customer representatives will respond as soon as possible..